The Indian Air Force’s first supersonic fighter, the MiG-21, which has served for approximately 62 years, is preparing for its final flight this year. The aircraft will be replaced by the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft Tejas Mk-1A and Tejas Mk-2, which are expected to form the backbone of India’s fighter fleet in the coming decades.
In India, the jet was assembled by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) with more than 1,200 MiG-21s having worn IAF roundels.
A veteran recalls the beginning
Air Marshal (retd) Brijesh Dhar Jayal, one of the first eight IAF pilots trained to fly the MiG-21 in the Soviet Union, recalled his first solo flight on the supersonic fighter in 1963, calling it “the beginning of a lifelong bond.” Now 90 and living in Dehradun, Jayal is among the last surviving members of the pioneering batch that introduced the aircraft into Indian service.
A new era in air power
In January 1963, at Lugovaya airbase in Kazakhstan, Jayal climbed into the cockpit of the MiG-21 for the first time. Thundering down the runway at 300 kmph, the jet lifted into the sky, marking the first solo MiG-21 flight by an IAF pilot.
That same year, Jayal co-founded No. 28 Squadron, the IAF’s first MiG-21 unit. He flew the first brand-new jet from Mumbai, where Russian technicians assembled the aircraft, to Chandigarh after a stopover in Agra.
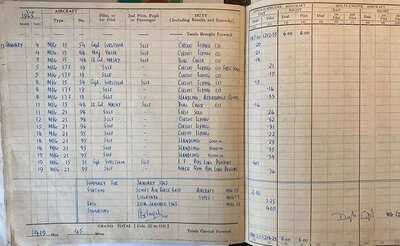
Training in the USSR
Jayal was selected in October 1962 along with Wing Commander Dilbagh Singh, Squadron Leaders M S D Wollen and S K Mehra, and Flight Lieutenants A K Mukherjee, H S Gill, A K Sen and D Keelor. The group underwent four months of training in the Soviet Union, starting with six weeks of Russian language lessons and technical instruction.
Also Read: Retired Air Marshal says MiG-21 was not a 'Flying Coffin', recalls how it beat four US fighter jets in Pakistan
“For the first six weeks, we didn’t even see the aircraft. We were immersed in learning Russian and studying the MiG’s systems in detail,” Jayal recalled. All radio communication was required to be in Russian. Training took place in sub-zero conditions, often dropping to minus 20 degrees Celsius.
Cut off from the outside world, the pilots only learned about the 1962 India-China war after their liaison officer mentioned it. Later, after negotiations, they managed to access radio broadcasts from AIR Jalandhar.
The Indian pilots initially trained on the MiG-15 and MiG-17 before transitioning to the MiG-21. According to Jayal, the Soviet training system was rigorous. “One must be grateful to the Soviet Union for having sustained a robust IAF by equipping it during a period of shortage of both resources and foreign exchange,” he said.
Flying coffin label rejected
Over the decades, the MiG-21 has been called the “flying coffin” due to its accident record. Jayal dismissed this description as “utter nonsense and completely unfair.”
“We had more MiG-21 squadrons than any other type, so naturally they featured more in accident statistics. But combat flying is not like driving a car — you cannot expect zero accidents. If you compare accident rates per 10,000 hours of flying, we were still better than many other air forces,” he said.
Also Read: Large touch screen, side joystick & less switches: Tejas Mk2 simulator provides first details look of India's 4.5 gen fighter jet
Looking back at the MiG-21’s service
Jayal said that while the MiG-21 was cutting-edge in its time, its design dated to the 1950s. “Like all good things, it must end. We have overused it, and technology has moved on. But in its time, it was cutting edge,” he said.
For him, the jet’s story was one of distinction. “It flew more, fought more, and served India with distinction. It was never a coffin, but a warrior. It never let us down in any war, any combat,” Jayal said.
(With inputs from TOI)
In India, the jet was assembled by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) with more than 1,200 MiG-21s having worn IAF roundels.
A veteran recalls the beginning
Air Marshal (retd) Brijesh Dhar Jayal, one of the first eight IAF pilots trained to fly the MiG-21 in the Soviet Union, recalled his first solo flight on the supersonic fighter in 1963, calling it “the beginning of a lifelong bond.” Now 90 and living in Dehradun, Jayal is among the last surviving members of the pioneering batch that introduced the aircraft into Indian service.
A new era in air power
In January 1963, at Lugovaya airbase in Kazakhstan, Jayal climbed into the cockpit of the MiG-21 for the first time. Thundering down the runway at 300 kmph, the jet lifted into the sky, marking the first solo MiG-21 flight by an IAF pilot.
That same year, Jayal co-founded No. 28 Squadron, the IAF’s first MiG-21 unit. He flew the first brand-new jet from Mumbai, where Russian technicians assembled the aircraft, to Chandigarh after a stopover in Agra.
Training in the USSR
Jayal was selected in October 1962 along with Wing Commander Dilbagh Singh, Squadron Leaders M S D Wollen and S K Mehra, and Flight Lieutenants A K Mukherjee, H S Gill, A K Sen and D Keelor. The group underwent four months of training in the Soviet Union, starting with six weeks of Russian language lessons and technical instruction.
Also Read: Retired Air Marshal says MiG-21 was not a 'Flying Coffin', recalls how it beat four US fighter jets in Pakistan
“For the first six weeks, we didn’t even see the aircraft. We were immersed in learning Russian and studying the MiG’s systems in detail,” Jayal recalled. All radio communication was required to be in Russian. Training took place in sub-zero conditions, often dropping to minus 20 degrees Celsius.
Cut off from the outside world, the pilots only learned about the 1962 India-China war after their liaison officer mentioned it. Later, after negotiations, they managed to access radio broadcasts from AIR Jalandhar.
The Indian pilots initially trained on the MiG-15 and MiG-17 before transitioning to the MiG-21. According to Jayal, the Soviet training system was rigorous. “One must be grateful to the Soviet Union for having sustained a robust IAF by equipping it during a period of shortage of both resources and foreign exchange,” he said.
Flying coffin label rejected
Over the decades, the MiG-21 has been called the “flying coffin” due to its accident record. Jayal dismissed this description as “utter nonsense and completely unfair.”
“We had more MiG-21 squadrons than any other type, so naturally they featured more in accident statistics. But combat flying is not like driving a car — you cannot expect zero accidents. If you compare accident rates per 10,000 hours of flying, we were still better than many other air forces,” he said.
Also Read: Large touch screen, side joystick & less switches: Tejas Mk2 simulator provides first details look of India's 4.5 gen fighter jet
Looking back at the MiG-21’s service
Jayal said that while the MiG-21 was cutting-edge in its time, its design dated to the 1950s. “Like all good things, it must end. We have overused it, and technology has moved on. But in its time, it was cutting edge,” he said.
For him, the jet’s story was one of distinction. “It flew more, fought more, and served India with distinction. It was never a coffin, but a warrior. It never let us down in any war, any combat,” Jayal said.
(With inputs from TOI)
You may also like

'Inaccurate, very expensive, and seriously controversial': Why does Donald Trump want to 'get rid of' mail-in ballots before the 2026 midterm election?

Keep Qatar safe: How to quickly report crimes using the Metrash mobile app

Love Island star announces her pregnancy as she shares gender reveal during Dubai holiday

Hyundais Class-Defining Creta SUV

Mammootty's Health Update: Superstar Recovers After Illness







